What Is FMEA?
Failure mode and Effect Analysis is a process analysis method for identifying potential failures in a design, manufacturing process, product, or service. The term “failure mode” refers to the various ways in which a process may fail. “Effects analysis” investigates the consequences of those failures. FMEA was first used by the US Military in the 1940s to improve the reliability and safety of military systems and equipment. Today, FMEA finds applications in various sectors including healthcare, technology, and manufacturing.
The FMEA is a proactive approach to risk management. It can be applied to certain processes within an organization, or for the entire organization at large. Again, in practice, I’ve only seen FMEA being applied to certain processes (as a quality assurance technique), and considering that it can be time-consuming, I’ll recommend applying it to value-adding operations first before scaling across the board.
Understanding the Elements of an FMEA
The diagram below is an example of an FMEA template.
Above the table, you can provide additional information about:
Project / Process / System (Indicate which project, process, or system, you want to analyze)
Date:
Prepared by:
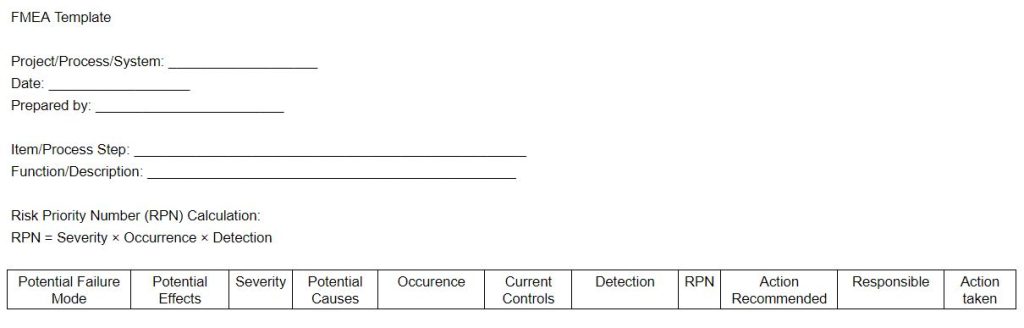
Then Label columns as follows:
- Potential Failure Mode
- Potential Effects
- Severity
- Potential Causes
- Occurrence
- Current Controls
- Detection rating
- RPN
- Action recommended
- Responsible
- Action taken
Process Name
This is the main topic of the FMEA. It might be a product, a manufacturing process, a system, or any component under investigation for possible failure.
For example, the process could be a search function on a data portal.
Potential Failure Mode
Whatever constitutes a state of failure as far as a process is concerned. So, for example, a user enters a certain search query into a search engine and clicks, the search button. If nothing happens, then that’s a possible failure in the process. The failure mode is whatever constitutes a deviation from pre-determined expectations of a process.
Potential Effects
For each failure mode identified, list the potential effects on the system or users. This could be in terms of loss of value to users, effects on dependent processes, or even financial losses.
Severity
Give each failure mode a severity score based on its potential effects. The rating is usually done on a scale of one to ten (with ten being the highest rating). Severity ratings would require everyone’s contributions and should be inferred based on some analogous or historical data.
Potential Causes
For each failure mode, itemize factors that could have contributed to the failure. It’s always useful to probe the team to uncover the root cause of each failure, so using the “why analysis” technique can be useful. Failure is generally due to these main factors; people (including training and technical know-how), process (technical and operational process flaws), product ( a product could just be prone to defect by their very nature), machine or equipment. Therefore it’s important to consider these factors in your assessment.
Occurrence
This refers to the likelihood or frequency of each failure mode occurring. Also on a scale of one to ten.
Current Controls
This refers to existing controls or methods in place to detect the failure mode or contributing factors.
Detection Rating
Also on a scale of one to ten, this refers to the ease of detecting deviations in the current control mechanisms.
The Risk Priority Number (RPN)
The RPN = severity x occurrence x detection rating
Calculate this score by multiplying the severity, occurrence, and detection rating for each failure mode. The highest priority is given to the failure mode with the highest score.
Recommended action(s)
Based on the RPN scores, brainstorm and agree on corrective actions or recommendations. Recommended actions should have due dates to keep people accountable and ensure actions are taken on time.
Responsible
This means assigning the responsibility of implementing an action or set of actions to a person or team in the organization.
Action(s) Taken
Because an FMEA report is a living document, as actions are completed, the document’s owner must keep it updated by noting when those actions were done.
How to Set up an FMEA?
The FMEA is the responsibility of an individual or team. In most organizations, it would fall within the scope of work of the quality assurance personnel, the project management organization (PMO), or an operations specialist. It is a tool for measuring operational KPIs and there should be a goal for running an FMEA otherwise, it might not be sustainable.
- Choose the Process or System: Decide the system, product, or process you want to use FMEA to assess.
- Assemble a cross-functional team: This includes people who can contribute their experience and expertise or who play a role in implementing the process in scope.
- Break down a large process into smaller components: Break the chosen process down into smaller parts or sections. it is simpler to recognize possible failure modes at each step rather than examining the process in its entirety.
- Review and update: Regularly updating and revising the FMEA allows organizations to incorporate new knowledge, lessons gained, and changing situations. This cycle of continuous development ensures that risk assessment remains relevant and effective throughout time.
Drawbacks of FMEA
The main drawback of the FMEA is how much time it takes to manage and follow up on recommended actions. Consider the following to manage time when running an FMEA.
Prioritization
Concentrate on crucial areas with the greatest potential impact. Prioritize failure modes based on severity, occurrence, and detection ratings (RPN) and tackle those areas first.
Preparation
Before each FMEA session, gather relevant data and information. The availability of data removes the need for substantial collection during meetings, saving time.
Timeboxing
Time box each FMEA update meeting. This ensures focused discussions and keeps them from getting too detailed and time-consuming.